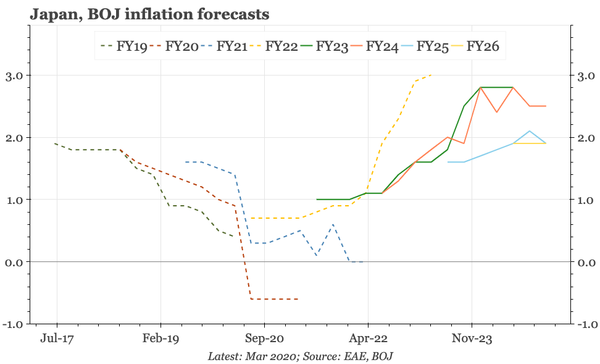
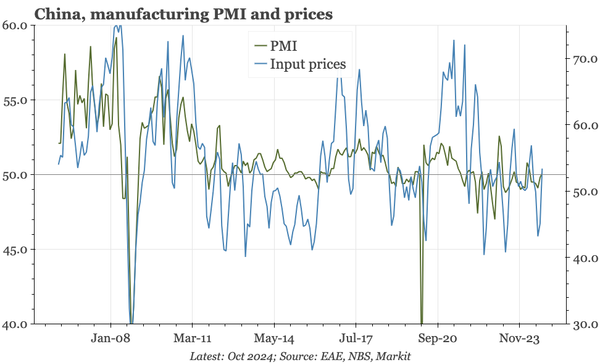
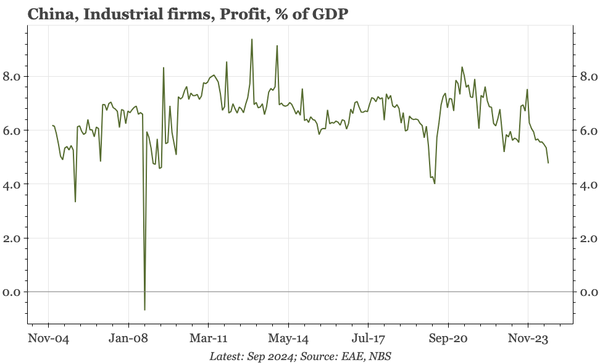
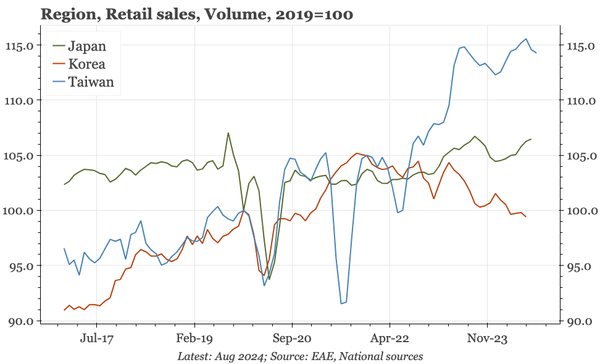
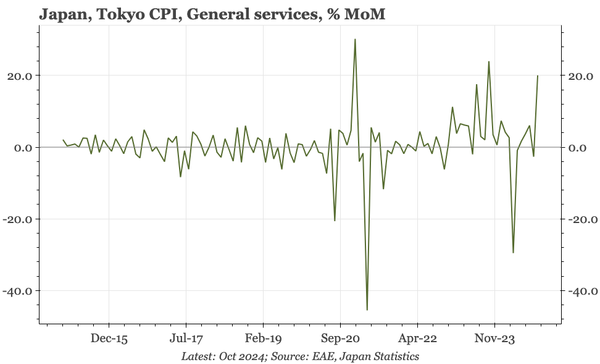
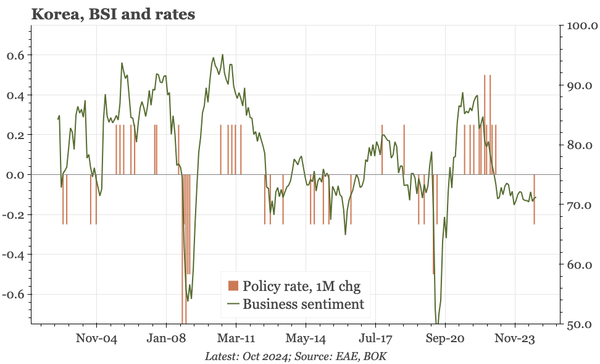
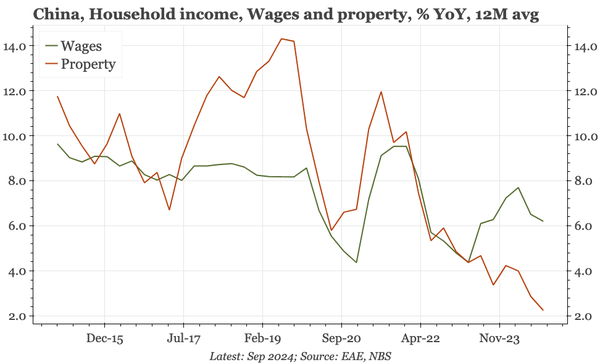
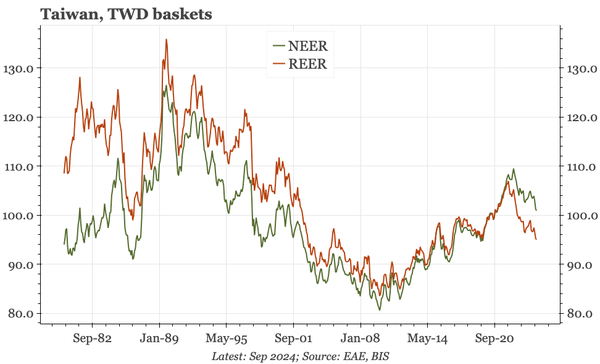
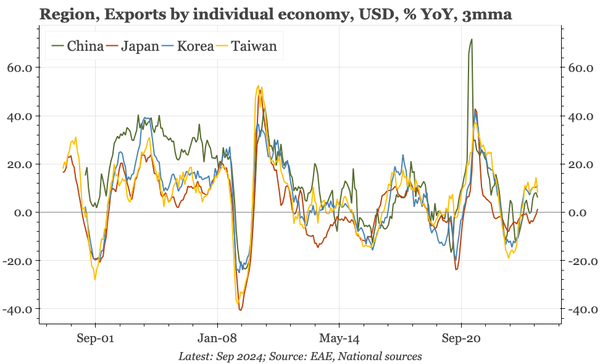
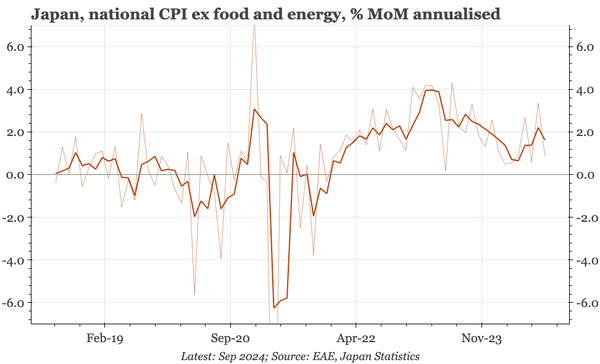
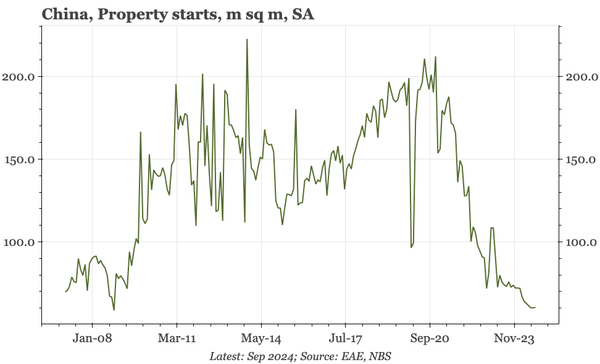
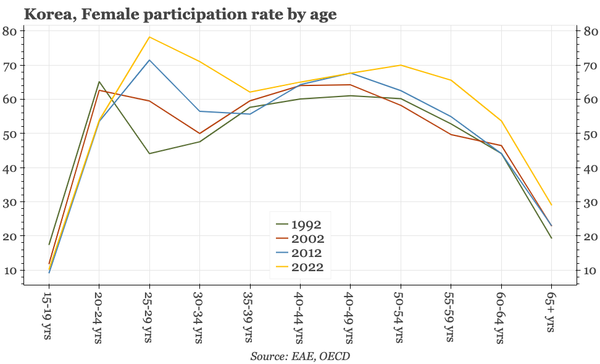
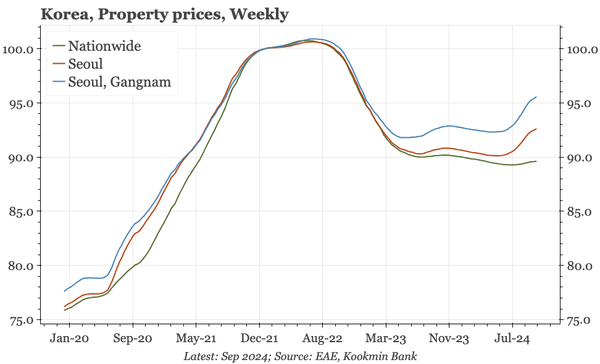
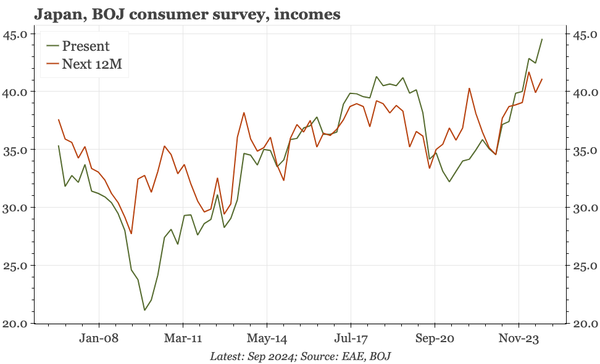
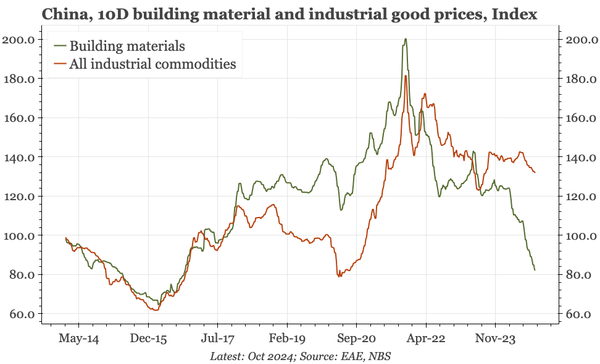
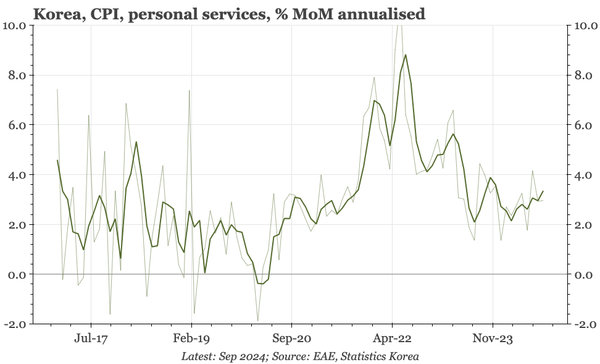
China – what have we learnt?
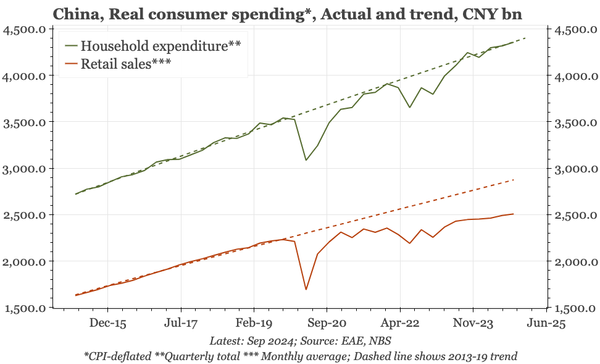
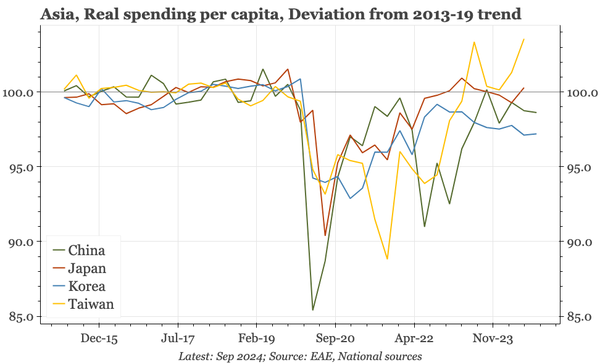
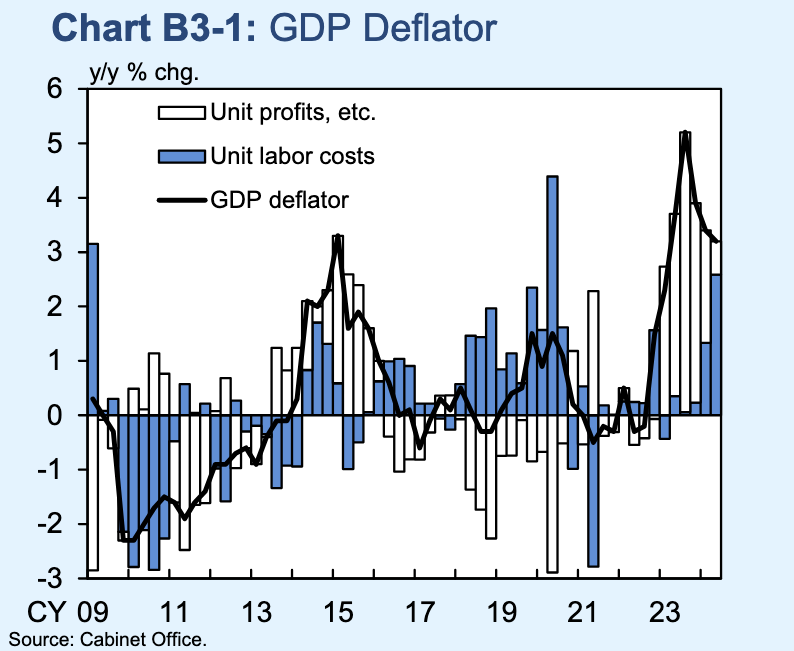
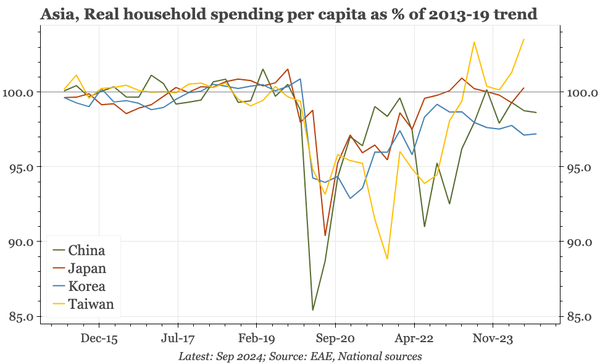
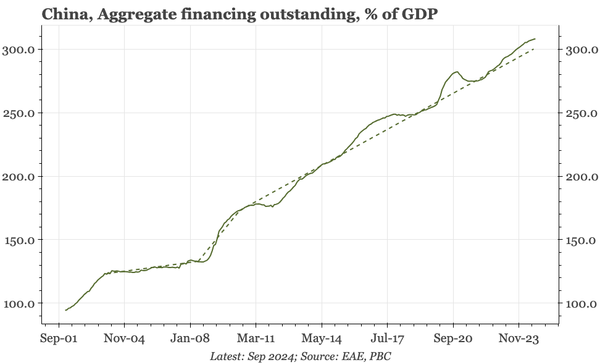
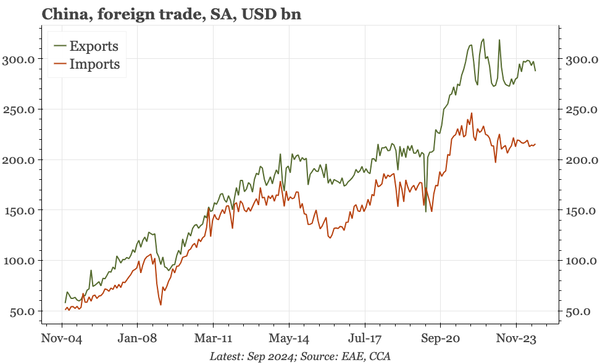
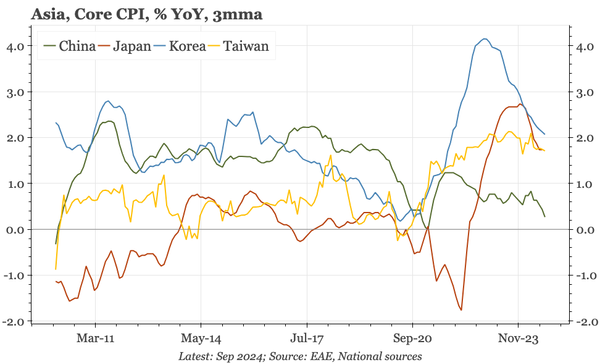
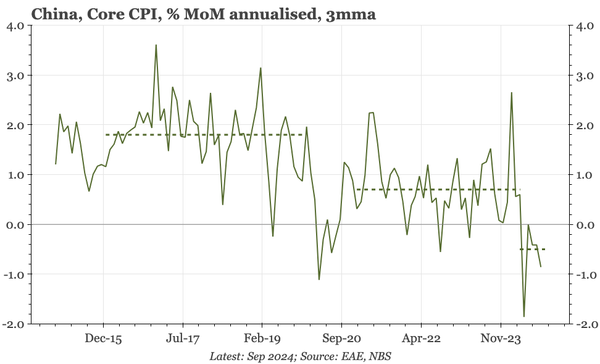
The bond swap does represent substantive policy. But there still isn't support for consumption, so this does look like an effort to put a floor under growth, rather than produce a new upcycle. And while that will probably be successful, stability will be endangered by a new round of Trump tariffs.