China – Q4 pick-up already fading

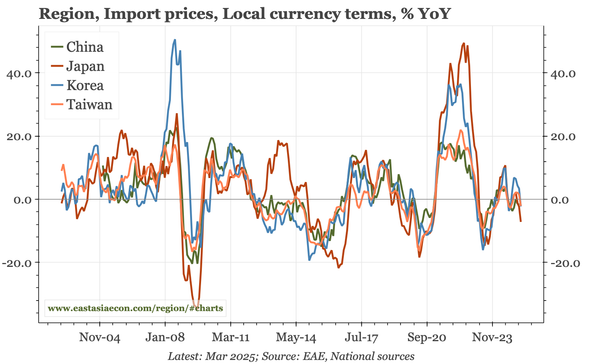
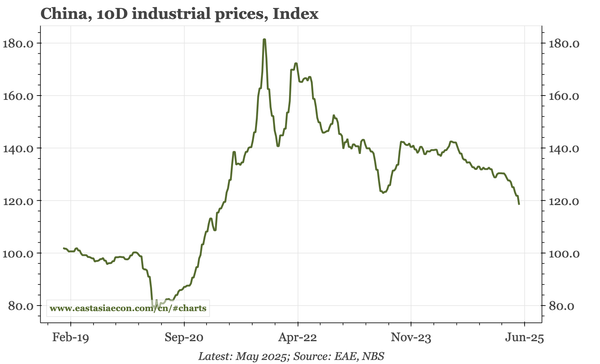
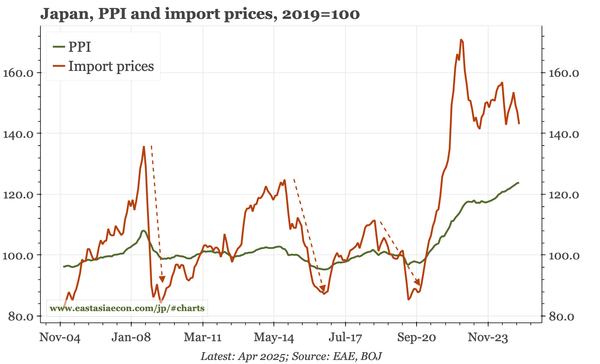
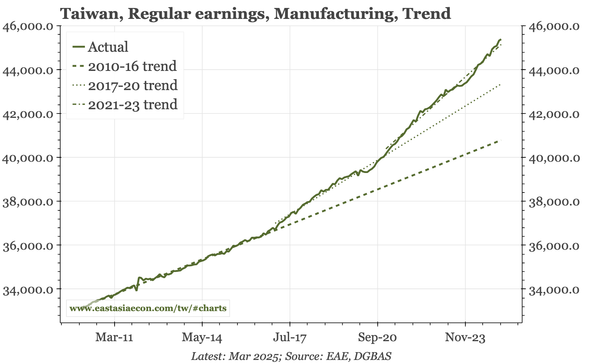
Headline YoY data are still benefiting from the Q4 pick-up, meaning another 5% growth quarter is likely. But sequentially, growth is slowing again, with no sign of any turnaround in construction that might put a sustainable floor under the overall economy.